Game-Changing Psoriasis Treatment: The Latest Breakthrough of 2014
Psoriasis 2014 Drug
Looking for an effective psoriasis treatment in 2014? You’re in the right place. Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by red, scaly patches that can be itchy, painful, and cause discomfort. While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve the overall quality of life.
I. What is Psoriasis?
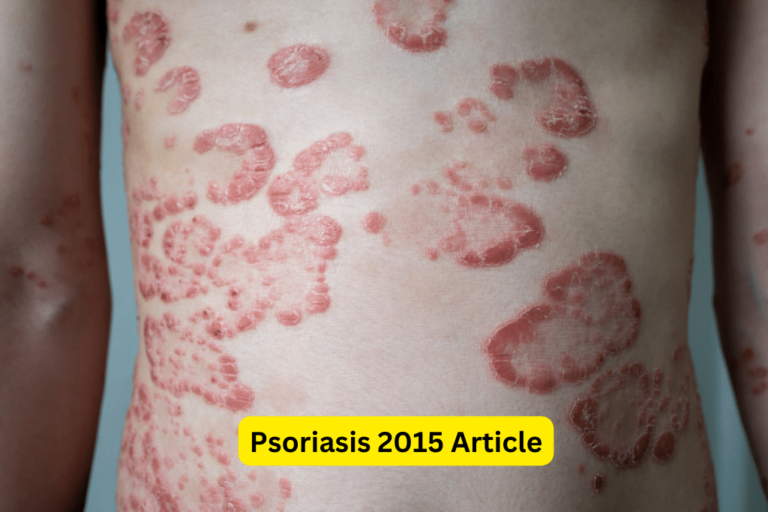
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes the rapid growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow deep within the skin and rise to the surface over a period of a few weeks. In psoriasis, this process is accelerated, causing cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin. This results in the formation of red, raised patches covered with white or silvery scales.
Psoriasis affects both men and women equally and can develop at any age. It is not contagious and can’t be transmitted from person to person. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers.
II. Traditional Treatment Approaches for Psoriasis
A. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. They are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and can help reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. Here are some common types of topical medications used:
1. Overview of topical medications
Topical medications come in various forms, including creams, ointments, gels, and lotions. They contain ingredients such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, coal tar, salicylic acid, and retinoids, among others.
2. Commonly prescribed topical corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that help reduce redness, itching, and inflammation. They are available in different strengths and forms, and your doctor will prescribe the appropriate one based on the severity of your psoriasis.
3. Calcitriol creams and ointments for mild psoriasis
Calcitriol is a synthetic form of vitamin D that helps slow down the growth of skin cells. It is often used for treating mild to moderate psoriasis and is available as a cream or ointment.
4. Anthralin and coal tar preparations for plaque psoriasis
Anthralin and coal tar are both traditional treatments for plaque psoriasis. Anthralin works by slowing down the growth of skin cells, while coal tar helps reduce the scaling and itching associated with psoriasis.
5. The role of moisturizers in managing psoriasis symptoms
Moisturizers play an essential role in managing psoriasis symptoms by hydrating the skin and reducing dryness. They can help reduce itching, scaling, and redness, and also improve the effectiveness of other treatments.
B. Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light to slow down the excessive growth of skin cells. It is an effective treatment option for moderate to severe psoriasis. Some commonly used phototherapy treatments include:
1. Introduction to phototherapy as a treatment option
Phototherapy uses different types of light to treat psoriasis, including natural sunlight, artificial UVB light, and psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy. It can help reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
2. Narrowband UVB therapy and its benefits
Narrowband UVB therapy uses a specific type of UVB light that is effective in treating psoriasis. It helps reduce inflammation, redness, and scaling, and can be done in a dermatologist’s office or at home with a prescribed light unit.
3. Photochemotherapy (PUVA) and its effectiveness
PUVA therapy combines the use of a prescription medication called psoralen with UVA light. Psoralen makes the skin more sensitive to light, allowing the UVA light to penetrate deeper and slow down the growth of skin cells.
4. Excimer laser therapy for targeting specific areas of psoriasis
Excimer laser therapy is a targeted form of phototherapy that delivers a high-intensity beam of UVB light to specific areas of psoriasis. It can be used to treat hard-to-reach areas or localized patches of psoriasis.
C. Systemic Medications
Systemic medications are prescription drugs that work throughout the body to treat psoriasis. They are typically reserved for moderate to severe cases that have not responded well to other treatments. Here are some commonly used systemic medications:
1. Overview of systemic medications for psoriasis
Systemic medications are available as pills, injections, or infusions. They work by suppressing the immune response and reducing inflammation in the body, which helps slow down the rapid growth of skin cells.
2. Methotrexate and its role in suppressing rapid skin cell growth
Methotrexate is an immunosuppressant medication that is often used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. It works by inhibiting the rapid division of skin cells and reducing inflammation.
3. Cyclosporine and its immunosuppressive effects
Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant drug that helps reduce the immune system’s response, thereby reducing inflammation and slowing down the growth of skin cells. It is typically used for short-term treatment due to potential side effects.
4. Acitretin for severe psoriasis cases
Acitretin is a retinoid medication that helps slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. It is often used in combination with other treatments for severe psoriasis.
5. Biologic drugs and their mechanisms of action
Biologic drugs are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis. They are typically given by injection or infusion and work by blocking specific proteins that contribute to the development of psoriasis.
III. Breakthrough Drug-Based Therapies in 2014
A. IL-17 Inhibitors
IL-17 inhibitors are a class of biologic drugs that target interleukin-17, a protein involved in the development of psoriasis. They have been shown to be highly effective in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
1. Mechanism of action and benefits of IL-17 inhibitors
IL-17 inhibitors work by blocking the action of interleukin-17, reducing inflammation and slowing down the growth of skin cells. They have shown significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life for patients with psoriasis.
2. Overview of available IL-17 inhibitors (Secukinumab, Ixekizumab, and Brodalumab)
Secukinumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab are the three FDA-approved IL-17 inhibitors for psoriasis treatment. They have shown high efficacy and safety profiles in clinical trials.
3. Clinical trials and efficacy data for IL-17 inhibitors
Clinical trials have shown that IL-17 inhibitors can achieve high rates of skin clearance and improvement in psoriasis symptoms. They have also demonstrated long-term benefits and durable responses in patients.
B. IL-23 Inhibitors
IL-23 inhibitors are another class of biologic drugs that target interleukin-23, a protein involved in the inflammatory process of psoriasis. They have shown promising results in clinical trials and are effective in treating moderate to severe psoriasis.
1. Understanding the role of IL-23 in psoriasis
IL-23 plays a crucial role in triggering and maintaining the inflammatory response in psoriasis. By blocking its action, IL-23 inhibitors can help reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
2. Overview of IL-23 inhibitors (Guselkumab and Risankizumab)
Guselkumab and risankizumab are two IL-23 inhibitors that have been approved for psoriasis treatment. They have demonstrated high rates of skin clearance and long-lasting results in clinical trials.
3. Comparative efficacy and safety profiles of IL-23 inhibitors
Both guselkumab and risankizumab have shown similar efficacy and safety profiles in clinical trials. They have been well-tolerated by patients and have minimal side effects.
C. PDE4 Inhibitors
PDE4 (phosphodiesterase 4) inhibitors are non-biologic oral medications that target inflammation in psoriasis. They work by blocking the enzyme PDE4, which is responsible for the production of inflammatory molecules in the body.
1. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors and their mode of action
PDE4 inhibitors specifically target the enzyme PDE4, which regulates the production of inflammatory molecules in the body. By blocking PDE4, these medications help reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells in psoriasis.
2. Apremilast: The first FDA-approved PDE4 inhibitor for psoriasis
Apremilast is the first and currently the only FDA-approved PDE4 inhibitor for the treatment of psoriasis. It has shown significant improvement in psoriasis symptoms, including skin clearance and reduction in itching.
3. Efficacy and side effects of apremilast
Apremilast has demonstrated high efficacy in clinical trials, with a significant number of patients achieving clear or almost clear skin. It is generally well-tolerated, with the most common side effects being diarrhea, nausea, and headache.
D. Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors
JAK inhibitors are a newer class of oral medications that target the Janus kinases, which are enzymes involved in the inflammatory response of psoriasis. They have shown promising results in clinical trials and offer an alternative treatment option for psoriasis.
1. Introduction to JAK inhibitors for psoriasis treatment
JAK inhibitors block specific enzymes involved in the immune response and inflammation of psoriasis. By inhibiting these enzymes, they help reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
2. Tofacitinib and its effectiveness in managing psoriasis symptoms
Tofacitinib is a JAK inhibitor that has been approved for the treatment of psoriasis. It has shown significant improvement in psoriasis symptoms, including skin clearance and reduction in itchiness.
3. Ongoing research and potential future JAK inhibitors for psoriasis
Research is currently ongoing to develop new JAK inhibitors for psoriasis treatment. These drugs have the potential to provide additional options for patients who do not respond to other treatments or experience side effects.
IV. Combination Therapies and Treatment Considerations
A. Combining topical treatments with systemic medications
Combining topical treatments with systemic medications can provide enhanced effectiveness in managing psoriasis. Topical medications can be used to target specific areas or stubborn patches of psoriasis, while systemic medications provide overall control of the disease.
B. Phototherapy as an adjunct to drug-based therapy
Phototherapy can be used as an adjunct to drug-based therapy to enhance the effectiveness of treatment. It can help reduce inflammation, clear stubborn patches, and extend periods of remission.
C. Personalized treatment approaches based on disease severity and patient factors
Psoriasis is a highly individualized condition, and treatment approaches should be tailored to each patient’s specific needs and preferences. Factors such as disease severity, overall health, lifestyle, and treatment history should be taken into account when determining the most appropriate treatment plan.
V. Managing Psoriasis Beyond Medications
A. Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
While medications play a crucial role in managing psoriasis, lifestyle modifications and home remedies can also help improve symptoms and overall well-being.
1. Importance of a healthy diet and weight management
A healthy diet and weight management can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties can be beneficial for people with psoriasis.
2. Stress reduction and its impact on psoriasis
Stress can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis flare-ups. Practicing stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help manage stress levels and improve psoriasis symptoms.
3. Natural remedies and their efficacy
Some natural remedies, such as aloe vera, tea tree oil, and oatmeal baths, have been found to provide relief from psoriasis symptoms. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
B. Supportive Therapies and Resources
Managing psoriasis can be challenging both physically and emotionally. Supportive therapies and resources can provide valuable assistance and improve overall well-being.
1. Importance of emotional support and counseling
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person’s mental and emotional well-being. Seeking emotional support from friends, family, or mental healthcare professionals can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with psoriasis.
2. Psoriasis support groups and online communities
Psoriasis support groups and online communities provide a platform for individuals with psoriasis to connect with others who share similar experiences. They can offer valuable support, information, and resources for managing psoriasis.
3. Professional organizations and resources for psoriasis patients
There are numerous professional organizations and resources available for individuals living with psoriasis. These organizations provide educational materials, treatment guidelines, and advocacy support for people with psoriasis.
Conclusion: Finding Relief with Psoriasis 2014 Drug Therapies
Psoriasis treatment has come a long way, and 2014 brought several breakthroughs in drug-based therapies. From IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors to PDE4 and JAK inhibitors, these medications have revolutionized the management of psoriasis and provided new hope for patients.
However, it’s important to remember that treatment approaches should be individualized, taking into account the severity of the disease, patient factors, and the potential for combination therapies. And while medications are essential, lifestyle modifications and supportive therapies play a significant role in managing psoriasis beyond medications.
Speak with your healthcare provider to discuss the best treatment options for you and take the necessary steps to regain control over your skin’s health and improve your overall well-being with the latest and most effective psoriasis treatments of 2014.
"Have You Seen Mike Walden's new holistic acne System yet? It's called "Acne No More" I've read the whole thing (all 223 pages) and there's some great information in there about how to naturally and permanently eliminate your acne without drugs, creams or any kind of gimmicks. I highly recommend it - it's very honest and straightforward without all the hype and b.s. you see all over the net these days. Here's the website where you can get more information:
Click Here -->AcneNoMore