Unmasking the Causes of Psoriasis: Insights and Solutions
Psoriasis Que Lo Causa
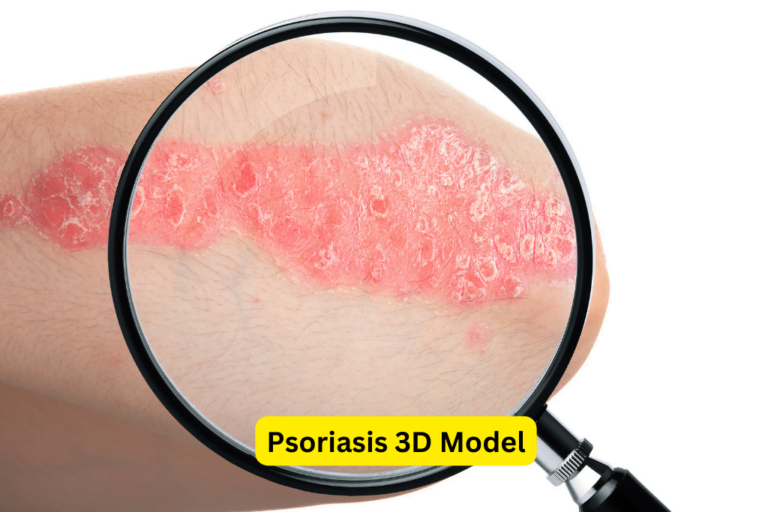
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and is characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches. It is estimated that approximately 2-3% of the world’s population suffers from psoriasis, making it a common and significant health concern. The impact of psoriasis goes beyond physical discomfort, as it can also have a considerable emotional and psychological toll on individuals.
There are several types of psoriasis, each with its own unique characteristics and symptoms. The most common type is plaque psoriasis, which manifests as raised, red plaques covered with white scales. Other types include guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
Causes of Psoriasis
Genetic Factors
Research has shown that there is a genetic susceptibility to psoriasis. Certain genes have been identified to be associated with the development of psoriasis, although the exact mechanism by which these genes contribute to the disease is not fully understood. Family history also plays a role, with individuals having a higher risk of developing psoriasis if they have a close relative with the condition.
Immune System Dysfunction
Another significant factor in the development of psoriasis is immune system dysfunction. In individuals with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly identifies healthy skin cells as foreign bodies and attacks them. This immune response leads to inflammation and the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in the characteristic plaques and scales seen in psoriasis.
T cells, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the immune response in psoriasis. These T cells become activated and produce cytokines, which are proteins that promote inflammation. The overproduction of these cytokines leads to ongoing inflammation and the perpetuation of the psoriatic process.
Various triggers can activate the immune response in individuals predisposed to psoriasis. These triggers include infections, such as strep throat, certain medications (e.g., lithium, antimalarial drugs), and injuries to the skin.
Environmental Triggers
In addition to genetic and immune system factors, environmental triggers can also contribute to the development and exacerbation of psoriasis. Stress and emotional factors have been shown to play a significant role in triggering psoriasis flares. Climate and weather conditions can also impact psoriasis, with some individuals experiencing improvement in symptoms during warm, sunny weather, while others may experience worsened symptoms in cold, dry climates.
Furthermore, certain medications, such as beta-blockers and antimalarial drugs, have been associated with psoriasis exacerbations. Infections, particularly streptococcal infections, can also trigger guttate psoriasis in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms and Signs of Psoriasis
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis, accounting for approximately 80-90% of cases. It is characterized by raised, red plaques covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques most commonly appear on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp. In addition to the physical symptoms, individuals with plaque psoriasis may also experience itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas.
Other Types of Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis typically appears as small, dot-like lesions on the trunk, limbs, and scalp. Inverse psoriasis affects the folds of the skin, such as the groin, armpits, and under the breasts. Pustular psoriasis is characterized by pus-filled blisters on the skin, accompanied by redness and tenderness. Erythrodermic psoriasis is a rare but severe form of psoriasis that affects the entire body, causing widespread redness, itching, and pain.
Diagnosing Psoriasis
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing psoriasis is primarily based on a clinical evaluation. Healthcare professionals will assess the appearance of the skin, looking for the characteristic plaques, scales, and redness associated with psoriasis. They will also take into account the presence of psoriasis-specific symptoms, such as itching, burning, and pain. Additionally, a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, including family history of psoriasis and any potential triggers, will be conducted.
Biopsy and Imaging Techniques
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis. During a biopsy, a small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope. This helps to rule out other skin conditions that may mimic psoriasis. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, may also be used in certain situations to assess the extent and severity of psoriasis.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the first line of defense in managing mild to moderate psoriasis. These include creams, ointments, and lotions that are applied directly to the affected areas. Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids are among the commonly prescribed topical treatments. They work by reducing inflammation, slowing down the excessive growth of skin cells, and relieving itching and other symptoms. Other topical treatments, such as tar preparations, salicylic acid, and moisturizers, can also be effective in managing psoriasis symptoms.
Systemic Medications
In cases where topical treatments are not sufficient, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. They come in oral or injectable forms. Immune-suppressing drugs, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, are often used in severe cases of psoriasis. Biologics, which are genetically engineered proteins, target specific components of the immune system and have shown high efficacy in treating psoriasis.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light to slow down the rapid growth of skin cells caused by psoriasis. This can be achieved through UVB or PUVA therapy. UVB therapy uses a specific range of UVB wavelengths to treat psoriasis, either through sunlight or artificial UVB lamps. PUVA therapy combines the use of psoralen, a medication that makes the skin more sensitive to UV light, with UVA exposure. Phototherapy can help to alleviate symptoms and induce remission in some individuals. However, it should be carefully monitored, as excessive UV exposure can increase the risk of skin cancer.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some individuals may seek alternative or complementary therapies to manage their psoriasis. Natural remedies such as aloe vera and fish oil have been suggested to have anti-inflammatory properties and may provide relief for some individuals. Other approaches include acupuncture, meditation, and dietary modifications. However, it is important to note that these therapies have varying levels of scientific evidence supporting their efficacy, and individuals should consult with their healthcare provider before incorporating them into their treatment plan.
Lifestyle Management and Coping Strategies
Moisturizing and Skincare
Maintaining proper skincare and moisturizing routines is essential for individuals with psoriasis. Moisturizers help to relieve dryness and itching, and can also act as a protective barrier for the skin. It is important to choose skincare products that are gentle and non-irritating, preferably ones specifically formulated for sensitive skin or psoriasis.
Stress Management
Stress reduction plays a crucial role in managing psoriasis symptoms. Stress can worsen existing plaques and trigger new flare-ups. Engaging in stress-relief techniques, such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy, can help to lower stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Diet and Nutrition
While the impact of diet on psoriasis is still under investigation, certain dietary factors may influence the condition. It is generally recommended to avoid or limit foods that can potentially trigger or worsen inflammation, such as processed foods, alcohol, and sugary snacks. On the other hand, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, may be beneficial for individuals with psoriasis.
Seeking Professional Support for Psoriasis
Dermatologist’s Role
Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial for individuals with psoriasis. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating skin conditions, including psoriasis. They can develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs, monitor the progress of the condition, and make adjustments as necessary. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist are essential for managing psoriasis effectively.
Emotional Support and Counseling
Living with psoriasis can have a significant emotional impact on individuals. Seeking emotional support through psychotherapy or joining support groups can provide a safe space to share experiences, gain insights, and develop coping strategies. Mental health professionals can offer guidance and support in dealing with the emotional challenges that can arise from living with psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex and multifaceted skin condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment options are crucial in managing psoriasis effectively. It is important to remember that treatment approaches may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s unique circumstances. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adopting effective lifestyle management strategies, individuals with psoriasis can find relief and regain control over their skin health.
"Have You Seen Mike Walden's new holistic acne System yet? It's called "Acne No More" I've read the whole thing (all 223 pages) and there's some great information in there about how to naturally and permanently eliminate your acne without drugs, creams or any kind of gimmicks. I highly recommend it - it's very honest and straightforward without all the hype and b.s. you see all over the net these days. Here's the website where you can get more information:
Click Here -->AcneNoMore