Understanding Psoriasis: Ask the Experts – Psoriasis FAQs: Expert Answers
Psoriasis Questions And Answers
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing red, itchy, and inflamed patches. It is a common skin disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Psoriasis is characterized by an overactive immune system which causes skin cells to grow rapidly, resulting in the buildup of thick, scaling patches on the skin’s surface. While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Prevalence and Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects approximately 2-3% of the global population, with both men and women being equally susceptible to the condition. It can develop at any age, but it most commonly appears between the ages of 15 and 35. The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Common Misconceptions about Psoriasis:
- Psoriasis is contagious: Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
- Psoriasis is just a skin condition: Psoriasis is not merely a skin condition. It is a chronic autoimmune disease that can have a significant impact on a person’s overall health and well-being.
- Psoriasis is caused by poor hygiene: Psoriasis is not caused by poor hygiene or lack of cleanliness. It is a complex condition that involves an immune system dysfunction.
- Psoriasis is only a cosmetic concern: Psoriasis can have a profound impact on a person’s psychological and emotional well-being. It is more than just a cosmetic concern.
Understanding the Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis can manifest in different forms, and the symptoms may vary from person to person. The most common types of psoriasis include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis:
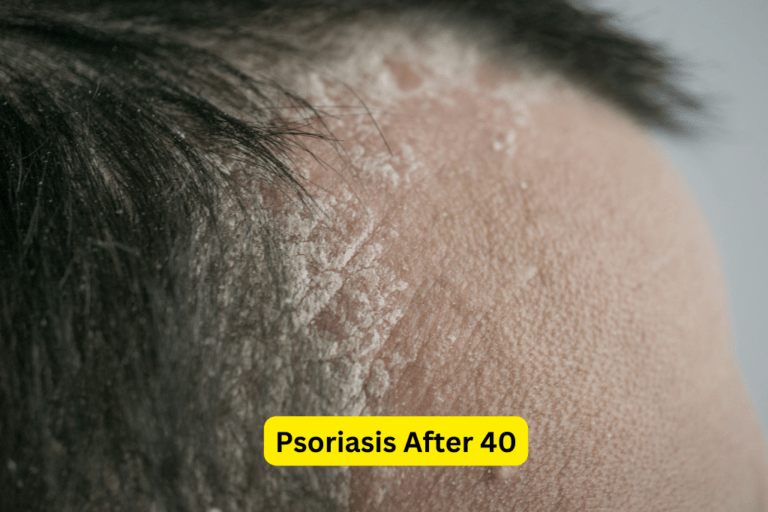
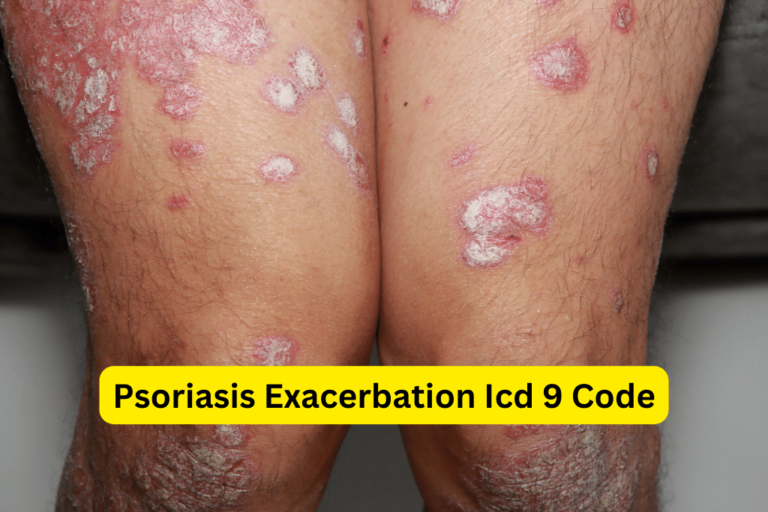
- Red, Itchy, and Inflamed Skin: Psoriasis typically presents as red, raised patches of skin that may be itchy and inflamed.
- Silvery Scales and Plaques: The affected areas of the skin often develop silvery scales or plaques, which can be easily scraped off.
- Dry, Cracked, and Bleeding Skin: Psoriasis can cause the skin to become dry, cracked, and may result in bleeding or pain.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: In some cases, psoriasis can affect the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Diagnosing Psoriasis
The diagnosis of psoriasis is usually based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, diagnostic tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination: The healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, any family history of psoriasis, and perform a thorough examination of your skin and nails.
Diagnostic Tests for Psoriasis: In certain cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis and rule out any other skin conditions.
Differentiating Psoriasis from Other Skin Conditions: Psoriasis can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions, such as eczema or fungal infections. A correct diagnosis is essential to establish the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, several treatment options aim to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals living with psoriasis. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of the disease.
Topical Treatments for Psoriasis:
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. These include:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications help reduce redness, itching, and inflammation of the skin.
- Vitamin D Analogs: These synthetic forms of vitamin D help slow down the growth of skin cells, reducing the scaling and inflammation associated with psoriasis.
- Retinoids: Retinoids are topical derivatives of Vitamin A that help regulate skin cell growth and improve the appearance of psoriasis plaques.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: These topical medications help reduce inflammation and are often used in sensitive areas such as the face and genitals.
Systemic Medications for Psoriasis:
Systemic medications are prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis that is resistant to topical treatments. These medications work internally to suppress the overactive immune response that triggers psoriasis.
- Methotrexate: Methotrexate is an oral medication that helps slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Cyclosporine suppresses the immune system and helps alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis.
- Biologic Drugs: Biologic drugs are injectable medications that target specific immune responses involved in psoriasis. They have shown significant efficacy in managing moderate to severe psoriasis.
Phototherapy and Light Therapy for Psoriasis:
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to natural or artificial ultraviolet light, which helps slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies for Psoriasis:
While not a cure, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage psoriasis symptoms and reduce flare-ups. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can worsen psoriasis symptoms, so maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the severity of symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as stress, smoking, alcohol, certain medications, and specific foods can help manage psoriasis.
- Using moisturizers: Regularly moisturizing the skin can help soothe dryness and reduce scaling.
- Practicing stress management techniques: Stress can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, so practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions about Psoriasis
Can Psoriasis be Cured?
No, psoriasis cannot be cured, but there are treatments available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with psoriasis. It is a chronic condition that requires long-term management.
Is Psoriasis Contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious. It is an autoimmune disease and cannot be transmitted from person to person through direct contact.
How to Manage Psoriasis Triggers?
Psoriasis triggers can vary from person to person, but some common triggers include stress, certain medications, infections, smoking, alcohol, and cold weather. Managing these triggers involves identifying them through self-awareness and making necessary lifestyle changes or avoiding them whenever possible.
Can Psoriasis Affect Other Parts of the Body?
Yes, psoriasis can affect other parts of the body, not just the skin. It can also affect the scalp, nails, joints, and even the mucous membranes.
What are the Potential Complications of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is not just a skin condition; it can have several potential complications. Some of these include:
- Psoriatic arthritis: A significant percentage of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Cardiovascular disease: Psoriasis has been associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
- Depression and anxiety: Living with psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person’s psychological well-being, leading to depression and anxiety.
- Reduced quality of life: Psoriasis can affect a person’s self-esteem, social interactions, and overall quality of life. It is important to address these psychological aspects along with the physical symptoms.
Living with Psoriasis
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Psoriasis:
Living with psoriasis can be challenging not only physically but also emotionally. The visible plaques and the social stigma associated with the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, and even depression or anxiety.
Coping Strategies for Psoriasis Patients:
It is essential for individuals with psoriasis to develop coping strategies to manage the emotional and psychological impact of the condition. Some strategies include:
- Seeking support: Joining support groups, talking to friends or family, or seeking therapy can provide the necessary emotional support.
- Being proactive in treatment: Following a treatment plan and being actively involved in managing symptoms can help individuals regain a sense of control over their condition.
- Practicing self-care: Engaging in activities that bring joy, practicing relaxation techniques, and taking care of overall physical and mental well-being.
- Sharing experiences and raising awareness: Participating in advocacy efforts and sharing experiences with others can help raise awareness and reduce the stigma associated with psoriasis.
Support Groups and Resources for Psoriasis Patients:
There are several support groups and resources available for individuals with psoriasis. These organizations provide valuable information, resources, and a sense of community for those living with psoriasis.
Future Developments in Psoriasis Research
Current Research and Potential Breakthroughs:
Researchers are continuously studying psoriasis in the hopes of finding new and more effective treatments. Current research focuses on better understanding the immune mechanisms involved in psoriasis, developing targeted therapies, and exploring the role of genetics in the disease.
Promising Treatments on the Horizon:
There are several promising treatments on the horizon for psoriasis. These include new biologic drugs, targeted therapies, and innovative topical treatments. Researchers are also studying the use of advanced technology, such as gene therapy and stem cell therapy, for the treatment of psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin and can have a significant impact on a person’s overall well-being. It is important to understand the symptoms, available treatment options, and how to effectively manage the condition. By staying informed about the latest research and seeking support, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives and overcome the challenges associated with the condition.
"Have You Seen Mike Walden's new holistic acne System yet? It's called "Acne No More" I've read the whole thing (all 223 pages) and there's some great information in there about how to naturally and permanently eliminate your acne without drugs, creams or any kind of gimmicks. I highly recommend it - it's very honest and straightforward without all the hype and b.s. you see all over the net these days. Here's the website where you can get more information:
Click Here -->AcneNoMore