Advanced Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model for Treatment Understanding
Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
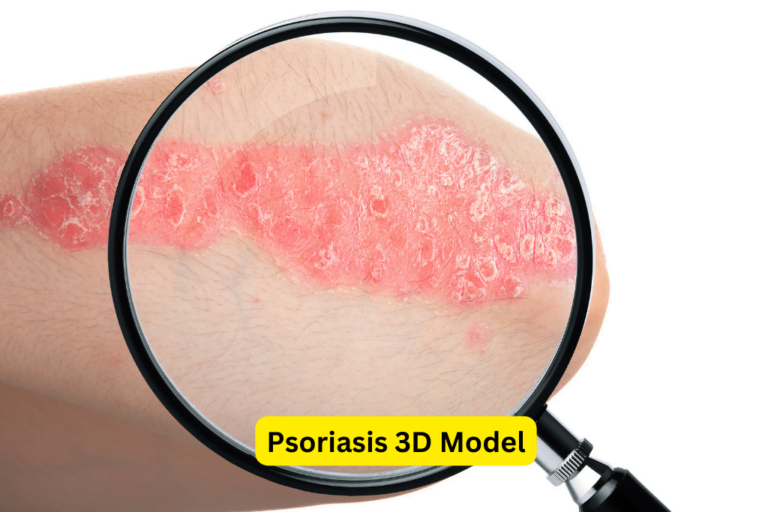
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by red, inflamed patches of skin that are often covered with silvery scales. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system. Studying psoriasis and developing effective treatments for it is of utmost importance for patients and researchers alike.
The objective of this article is to highlight the significance of utilizing a psoriasis xenograft mouse model in psoriasis research. This model provides a valuable tool for studying the disease and its underlying mechanisms, as well as for evaluating potential therapeutic compounds.
Understanding Psoriasis
A. Definition and Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by the rapid and excessive growth of skin cells. It is believed to be caused by both genetic and environmental factors. Triggers such as stress, infections, and certain medications can contribute to the development and exacerbation of psoriasis.
B. Types and Symptoms of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. The most common type is plaque psoriasis, which presents as raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. Symptoms of psoriasis can vary, but commonly include itching, pain, and discomfort.
C. Current Research and Treatments for Psoriasis
Significant advancements have been made in the understanding and treatment of psoriasis. Current research is focused on identifying the underlying mechanisms of the disease and developing targeted therapies. Treatments for psoriasis include topical medications, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologics that target specific aspects of the immune system.
D. Limitations of Existing Models in Studying Psoriasis
While various models exist for studying psoriasis, such as cell culture models and genetically engineered mouse models, they have certain limitations. These models often fail to fully recapitulate the complex pathogenesis and characteristics of human psoriasis.
Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model: An Overview
A. Explanation of Xenograft Mouse Models
Xenograft mouse models involve the transplantation of human tissue or cells into immunodeficient mice. This allows researchers to study human diseases in a more clinically relevant context.
B. Rationale for Using Xenograft Mouse Models in Psoriasis Research
The use of xenograft mouse models in psoriasis research provides a unique opportunity to study the disease in an in vivo setting. By grafting human psoriatic tissue onto mice, researchers can observe the development of psoriatic-like skin lesions and study the underlying mechanisms.
C. Steps Involved in Developing a Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
The development of a psoriasis xenograft mouse model involves several key steps. First, appropriate human psoriatic tissue must be selected and prepared for grafting. The tissue is then implanted onto the mice, and disease progression is carefully monitored and evaluated.
Establishing a Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
A. Selection of Appropriate Human Psoriatic Tissue
Choosing an appropriate source of psoriatic tissue is crucial for establishing an accurate xenograft mouse model. Tissue samples from patients with well-characterized psoriasis lesions are preferred.
B. Preparation of the Tissue for Grafting
The selected psoriatic tissue needs to be properly prepared for grafting onto the mice. This involves processing the tissue to obtain viable cells or explants that can be transplanted effectively.
C. Implantation of the Tissue into the Mouse Model
The prepared psoriatic tissue is then implanted onto the mice. This can be done by surgically grafting the tissue onto the back of the mice or utilizing other techniques such as injection or transplantation into subcutaneous pockets.
D. Monitoring Disease Progression in the Model
After implantation, the mice are closely monitored for the development of psoriatic-like skin lesions. Disease progression can be assessed through various methods such as histological analysis, gene expression studies, and evaluation of clinical symptoms.
Advantages of the Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
A. Recapitulation of Human Psoriasis Characteristics in Mice
The psoriasis xenograft mouse model has the unique ability to mimic many features of human psoriasis. This includes the development of psoriatic-like lesions, immune cell infiltration, and dysregulation of key pathways involved in psoriasis pathogenesis.
B. Possibility for Personalized Medicine and Drug Testing
The use of the psoriasis xenograft mouse model opens up possibilities for personalized medicine and drug testing. Researchers can evaluate the efficacy of novel therapeutic compounds in a clinically relevant context, potentially leading to more tailored and effective treatments for individual patients.
C. Potential Insights into the Pathogenesis and Mechanisms of Psoriasis
Studying psoriasis in a xenograft mouse model can provide valuable insights into the underlying pathogenesis and mechanisms of the disease. By observing the development of psoriatic-like lesions and analyzing gene expression changes, researchers can gain a better understanding of the factors contributing to the development and progression of psoriasis.
D. Comparison of the Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model to Other Models
When compared to other models, the psoriasis xenograft mouse model offers several advantages. It allows for the study of human psoriasis in a more clinically relevant context, as well as the evaluation of potential therapeutic interventions in a living organism.
Applications of the Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
A. Evaluating the Efficacy of Novel Therapeutic Compounds
The psoriasis xenograft mouse model can be used to assess the efficacy of novel therapeutic compounds. Researchers can evaluate the effects of different drugs on the development and progression of psoriatic-like lesions, allowing for the identification of potential new treatments.
B. Studying the Role of Specific Genes and Pathways in Psoriasis Development
This model also provides a valuable tool for studying the role of specific genes and pathways in psoriasis development. By manipulating gene expression or inhibiting key signaling pathways, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying the disease.
C. Investigating the Interaction Between Psoriasis and Other Diseases
Psoriasis is often associated with other systemic conditions such as psoriatic arthritis and cardiovascular disease. The psoriasis xenograft mouse model can be utilized to study the interaction between psoriasis and these comorbidities, potentially uncovering shared mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
D. Predicting Treatment Response in Patients with Psoriasis
By studying the response of psoriatic-like lesions in the xenograft mouse model to different treatments, researchers may be able to predict treatment response in patients with psoriasis. This can aid in the development of personalized treatment plans for individuals, leading to better outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of the Psoriasis Xenograft Mouse Model
A. Ethical Considerations in Using Animal Models
The use of animal models, including xenograft mouse models, raises ethical considerations. Researchers must ensure that animal welfare is prioritized and that alternative methods are explored whenever possible.
B. Variability and Reproducibility Issues
As with any research model, variability and reproducibility can pose challenges. The psoriasis xenograft mouse model may exhibit variability in disease progression, making it essential for researchers to carefully design and conduct their experiments to ensure reliable results.
C. Potential Differences Between Mouse and Human Immune Systems
While the psoriasis xenograft mouse model replicates some aspects of human psoriasis, there may still be differences between mouse and human immune systems. These differences can influence disease mechanisms and treatment responses, requiring cautious interpretation of results.
D. Overcoming Limitations and Future Directions for the Model
Despite its limitations, the psoriasis xenograft mouse model holds immense promise for advancing our understanding of psoriasis and developing more effective treatments. Future research should focus on standardizing protocols, increasing reproducibility, and exploring alternative animal models that better recapitulate human psoriasis.
Conclusion
The psoriasis xenograft mouse model offers a valuable tool for studying psoriasis and its underlying mechanisms. By utilizing this model, researchers can recapitulate key aspects of human psoriasis, investigate the effectiveness of potential therapies, and gain insights into the pathogenesis of the disease. While challenges and limitations exist, the psoriasis xenograft mouse model holds immense potential for advancing our understanding and treatment of psoriasis.
"Have You Seen Mike Walden's new holistic acne System yet? It's called "Acne No More" I've read the whole thing (all 223 pages) and there's some great information in there about how to naturally and permanently eliminate your acne without drugs, creams or any kind of gimmicks. I highly recommend it - it's very honest and straightforward without all the hype and b.s. you see all over the net these days. Here's the website where you can get more information:
Click Here -->AcneNoMore