Empowering Psoriasis at 70: Knowledge and Effective Treatment Options
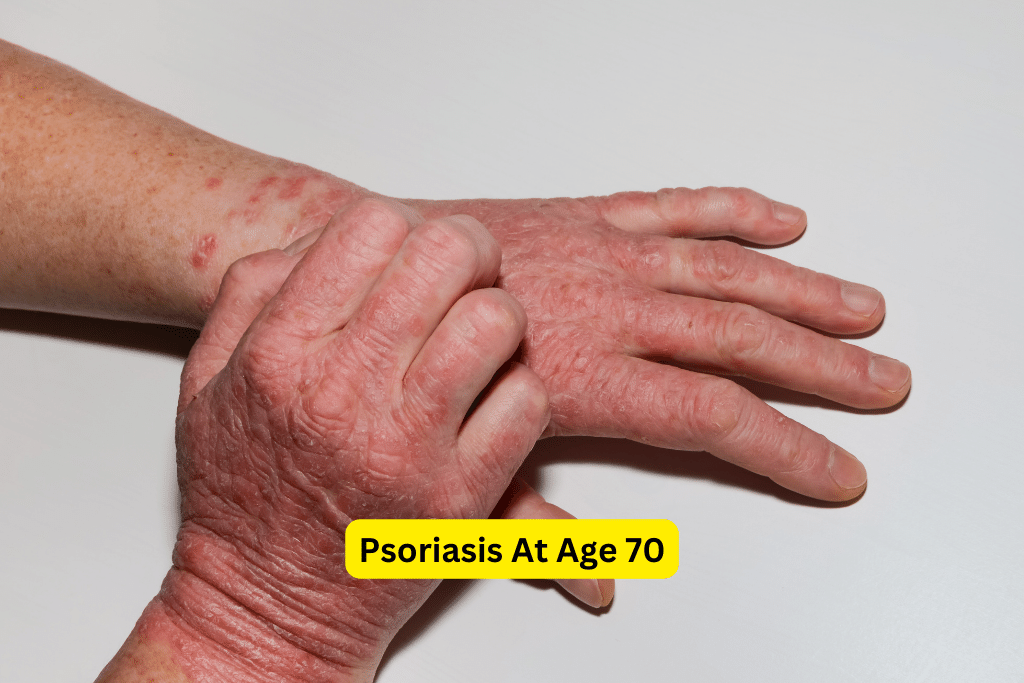
Psoriasis At Age 70
Understanding Psoriasis at Age 70: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing itchy, red, and scaly patches. While it can occur at any age, it can be especially challenging for individuals aged 70 and beyond. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for psoriasis in older adults. Understanding the condition and its impact on older individuals is vital for effective management and improving overall quality of life. Let’s dive in and explore the world of psoriasis in individuals aged 70 and beyond.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells on the surface. This excessive cell turnover leads to the formation of thick, red, and scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. Psoriasis is not contagious and is considered an autoimmune disease. This means that the immune system mistakenly identifies healthy skin cells as foreign invaders and triggers an inflammatory response.
In older adults, the most common types of psoriasis include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and inverse psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis is characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. Guttate psoriasis appears as small, teardrop-shaped lesions scattered across the body. Inverse psoriasis affects the skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, causing smooth, red patches.
While psoriasis can affect individuals of all ages, the prevalence tends to increase with age. Studies have shown that up to 3% of individuals aged 70 and above have psoriasis. The condition can significantly impact the physical and emotional well-being of older adults, affecting their quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Psoriasis has a multifactorial etiology, and both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Older adults with a family history of psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Age-related changes in the immune system can also contribute to the development or worsening of psoriasis in older individuals.
In addition to genetic predisposition and age-related immune changes, certain trigger factors can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms in older adults. These triggers may include stress, certain medications, infections, injury to the skin, and weather changes. Understanding and managing these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of psoriasis flare-ups.
Symptoms and Complications
Psoriasis can manifest in various ways, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. In older adults, common symptoms of psoriasis may include red, inflamed patches of skin, itching, scaling, and even pain. It is important to note that psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing pitting, discoloration, and crumbling.
Psoriasis in older adults can be associated with several complications. These may include joint pain and inflammation, known as psoriatic arthritis, which can significantly affect mobility and daily activities. Other complications may include cardiovascular issues, such as an increased risk of heart disease and stroke, as well as an increased risk of developing other autoimmune diseases.
The impact of psoriasis on quality of life cannot be overlooked. Older adults with psoriasis may experience social embarrassment, self-esteem issues, and even depression. It is crucial to address these psychological aspects and provide appropriate support and treatment for a holistic approach to psoriasis management.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
If you suspect you have psoriasis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Diagnosis is typically based on a thorough physical examination, medical history assessment, and evaluation of the affected skin. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be recommended to rule out other skin conditions.
Older individuals with psoriasis may have an increased prevalence of certain comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. It is important to undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation to monitor and manage these associated conditions effectively.
Treatment Options
The treatment for psoriasis in individuals aged 70 and beyond may vary depending on the severity and extent of the condition. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan.
A. Topical Treatments: Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for psoriasis management. These may include medicated creams, ointments, and lotions that help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. It is important to follow the prescribed regimen and be aware of potential side effects.
B. Phototherapy: Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is another treatment option that involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light. This therapy can help slow down the excessive growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. However, older adults should be cautious and consider potential risks, as they may have increased sensitivity to light.
C. Systemic Medications: In more severe cases of psoriasis, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications can be taken orally or administered through injections and work by suppressing the immune system. It is important to discuss potential side effects and monitoring requirements with a healthcare professional.
D. Other Treatment Modalities: In addition to conventional treatments, there are alternative therapies and complementary approaches that may provide relief for psoriasis symptoms. These may include natural remedies, such as moisturizers, oatmeal baths, and aloe vera. Physiotherapy techniques, such as ultraviolet therapy and balneotherapy, can also be beneficial. Lifestyle modifications, including stress management techniques, a balanced diet, and regular exercise, can contribute to overall symptom management.
Managing Psoriasis at Age 70: Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
In addition to medical interventions, certain lifestyle changes and self-care practices can help older adults manage their psoriasis effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest, can support the immune system and promote overall skin health.
For individuals with psoriasis, it is important to develop a proper skincare routine. This may include using gentle, fragrance-free products, moisturizing regularly, and avoiding harsh soaps or hot water that can further irritate the skin. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in enjoyable activities, can help reduce psoriasis flare-ups.
Supportive Resources for Older Adults with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can sometimes feel isolating. However, there are various resources available to provide support and guidance. Support groups and patient advocacy organizations dedicated to psoriasis can offer a sense of community, information sharing, and emotional support. Online communities and forums are also valuable platforms for connecting with others going through similar experiences.
The importance of social support and psychological well-being in managing psoriasis cannot be overstated. Engaging in activities with friends and loved ones, seeking professional counseling if needed, and prioritizing self-care can all contribute to a more positive outlook and improved quality of life.
Preventive Measures and Long-Term Outlook
While psoriasis is a chronic condition, there are steps that can be taken to prevent flare-ups and maintain overall skin health. Avoiding known triggers, such as stress and certain medications, can help minimize the occurrence of psoriasis symptoms. Protecting the skin from trauma, practicing good hygiene, and regularly moisturizing can also contribute to long-term management.
It is important to have realistic expectations regarding the long-term outlook for psoriasis at age 70. With proper medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and access to supportive resources, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives. While there is no cure for psoriasis, effective management strategies can help minimize symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
Psoriasis can be a challenging condition, especially for individuals aged 70 and beyond. However, with awareness, proper medical care, and lifestyle adjustments, older adults can effectively manage their psoriasis and enjoy a fulfilling life. Seeking professional guidance, connecting with support groups, and prioritizing self-care are essential steps in the journey towards alleviating the physical and emotional burden of psoriasis. Remember, you are not alone, and there is hope for living well with psoriasis at age 70 and beyond.
"Have You Seen Mike Walden's new holistic acne System yet? It's called "Acne No More" I've read the whole thing (all 223 pages) and there's some great information in there about how to naturally and permanently eliminate your acne without drugs, creams or any kind of gimmicks. I highly recommend it - it's very honest and straightforward without all the hype and b.s. you see all over the net these days. Here's the website where you can get more information:
Click Here -->AcneNoMore